# 3968
The CDC has posted FluView for week 43, ending October 30th, 2009. The level of activity we are seeing is roughly what we might expect during the height of the flu season, not during late October.
I’ve excerpted some of the data and graphs below, but follow the link to read it in its entirety.
2009-2010 Influenza Season Week 43 ending October 31, 2009
All data are preliminary and may change as more reports are received.
Synopsis:
During week 43 (October 25-31, 2009), influenza activity remained elevated in the U.S.
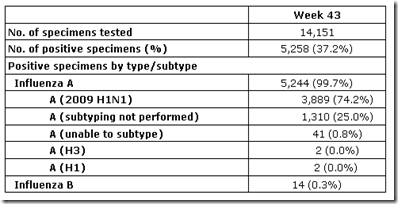
- 5,258 (37.2%) specimens tested by U.S. World Health Organization (WHO) and National Respiratory and Enteric Virus Surveillance System (NREVSS) collaborating laboratories and reported to CDC/Influenza Division were positive for influenza.
- Over 99% of all subtyped influenza A viruses being reported to CDC were 2009 influenza A (H1N1) viruses.
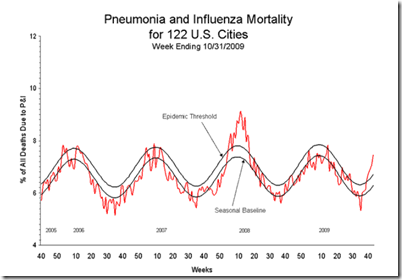
- The proportion of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza (P&I) was above the epidemic threshold.
- Eighteen influenza-associated pediatric deaths were reported. Fifteen of these deaths were associated with 2009 influenza A (H1N1) virus infection and three were associated with an influenza A virus for which the subtype was undetermined.
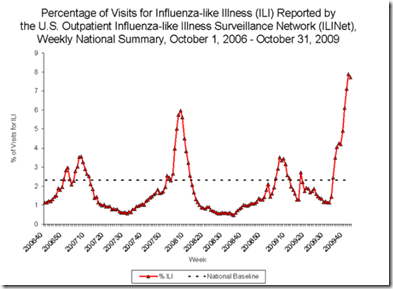
- The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was above the national baseline. All 10 regions reported ILI above region-specific baseline levels.
- Forty-eight states reported geographically widespread influenza activity, two states reported regional influenza activity, the District of Columbia reported local influenza activity; Puerto Rico and Guam reported sporadic influenza activity, and the U.S. Virgin Islands did not report.
U.S. Virologic Surveillance:
WHO and NREVSS collaborating laboratories located in all 50 states and Washington D.C., report to CDC the number of respiratory specimens tested for influenza and the number positive by influenza type and subtype. The results of tests performed during the current week are summarized in the table below.
Pneumonia and Influenza (P&I) Mortality Surveillance
During week 43, 7.4% of all deaths reported through the 122-Cities Mortality Reporting System were due to P&I. This percentage was above the epidemic threshold of 6.7% for week 43. Including week 43, P&I mortality has been above threshold for five consecutive weeks.
Influenza-Associated Pediatric Mortality
Eighteen influenza-associated pediatric deaths were reported to CDC during week 43 (California [8], Indiana, Louisiana [2], Mississippi, New York, Oklahoma, Texas [2], Virginia, and West Virginia). Fifteen of these deaths were associated with 2009 influenza A (H1N1) virus infection and three were associated with an influenza A virus for which the subtype is undetermined.
These deaths occurred between July 12 and October 31, 2009. Seven deaths reported during week 43 occurred during the 2008-09 season, bringing the total number of reported pediatric deaths occurring during that season to 124. Since August 30, 2009, CDC has received 85 reports of influenza-associated pediatric deaths that occurred during the current influenza season (12 deaths in children less than 2 years old, nine deaths in children 2-4 years old, 30 deaths in children 5-11 years old, and 34 deaths in individuals 12-17 years old).
Outpatient Illness Surveillance:
Nationwide during week 43, 7.7% of patient visits reported through the U.S. Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network (ILINet) were due to influenza-like illness (ILI). This percentage is above the national baseline of 2.3%.